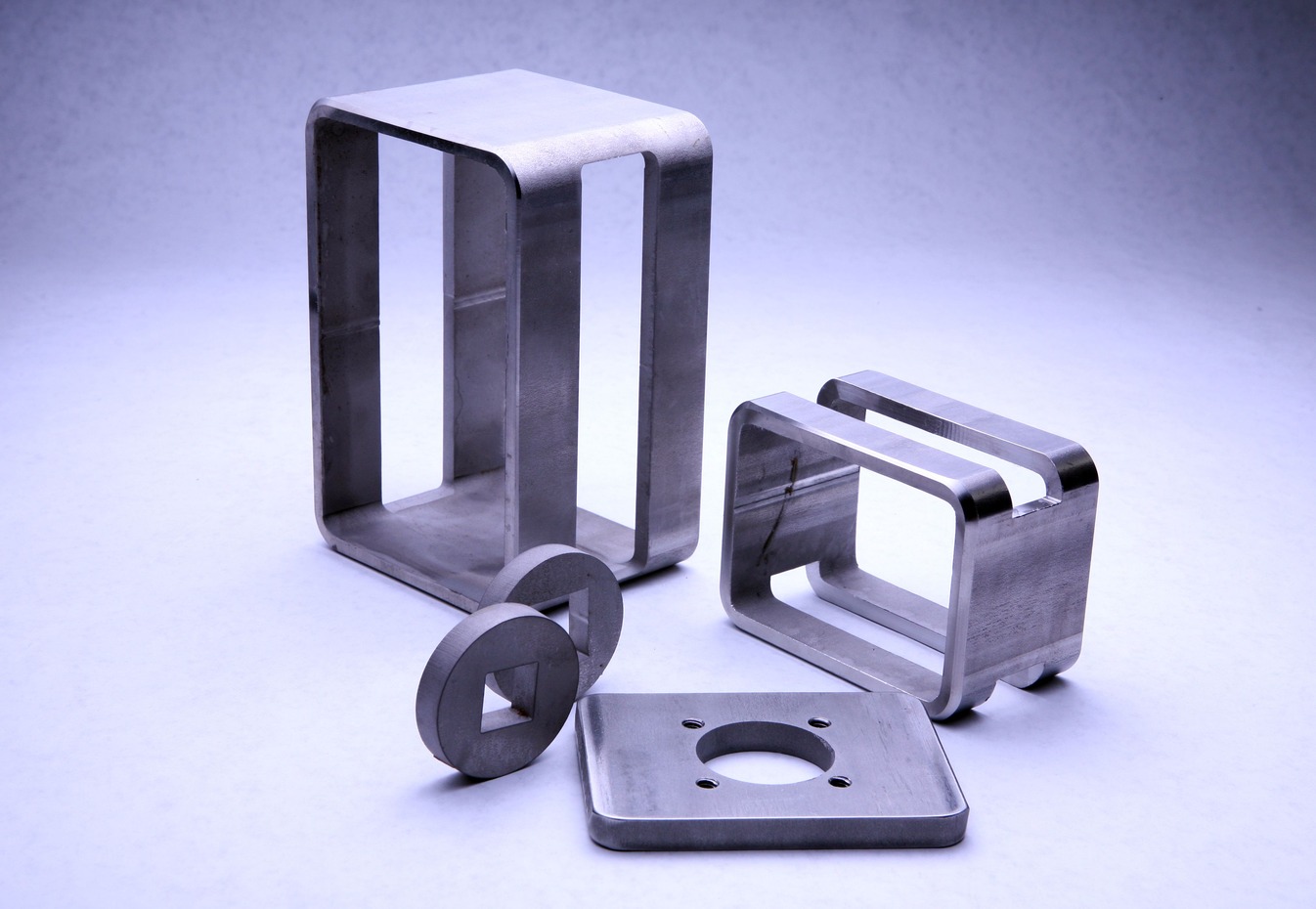
Welcome to SchGo’s guide to quality control and inspection methods for precision engineering. In the realm of precision engineering, quality is paramount. Every component must meet exacting standards of accuracy, reliability, and consistency to ensure optimal performance and customer satisfaction. In this guide, we’ll explore essential quality control techniques and inspection methods that will help you uphold the highest standards of quality in your precision engineering projects.
Understanding Quality Control and Inspection: Quality control is a systematic process that involves monitoring and maintaining the quality of products throughout the manufacturing process. Inspection, on the other hand, is the act of examining products to ensure they meet specified requirements and standards. Together, quality control and inspection play a crucial role in identifying defects, preventing errors, and ensuring that only high-quality products reach the customer.

Essential Quality Control and Inspection Methods:
- Dimensional Analysis: Dimensional analysis involves measuring the physical dimensions of a component to ensure it meets specified tolerances and requirements. Techniques such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), optical comparators, and digital calipers are commonly used to perform dimensional analysis and verify the accuracy of critical dimensions.
- Surface Finish Evaluation: Surface finish evaluation assesses the surface texture and appearance of a component to ensure it meets aesthetic and functional requirements. Common methods for evaluating surface finish include visual inspection, profilometers, and surface roughness testers. By quantifying surface roughness and texture, engineers can ensure that components meet design specifications and perform as intended.
- Mechanical Testing: Mechanical testing involves subjecting components to various mechanical stresses and loads to assess their mechanical properties and performance characteristics. Common mechanical tests include tensile testing, hardness testing, and impact testing, which provide valuable insights into the strength, toughness, and durability of materials and components.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques allow engineers to inspect components for defects and flaws without causing damage to the material. Common NDT methods include ultrasonic testing, radiographic testing, magnetic particle testing, and dye penetrant testing, which can detect defects such as cracks, voids, and discontinuities that may compromise the integrity of the component.
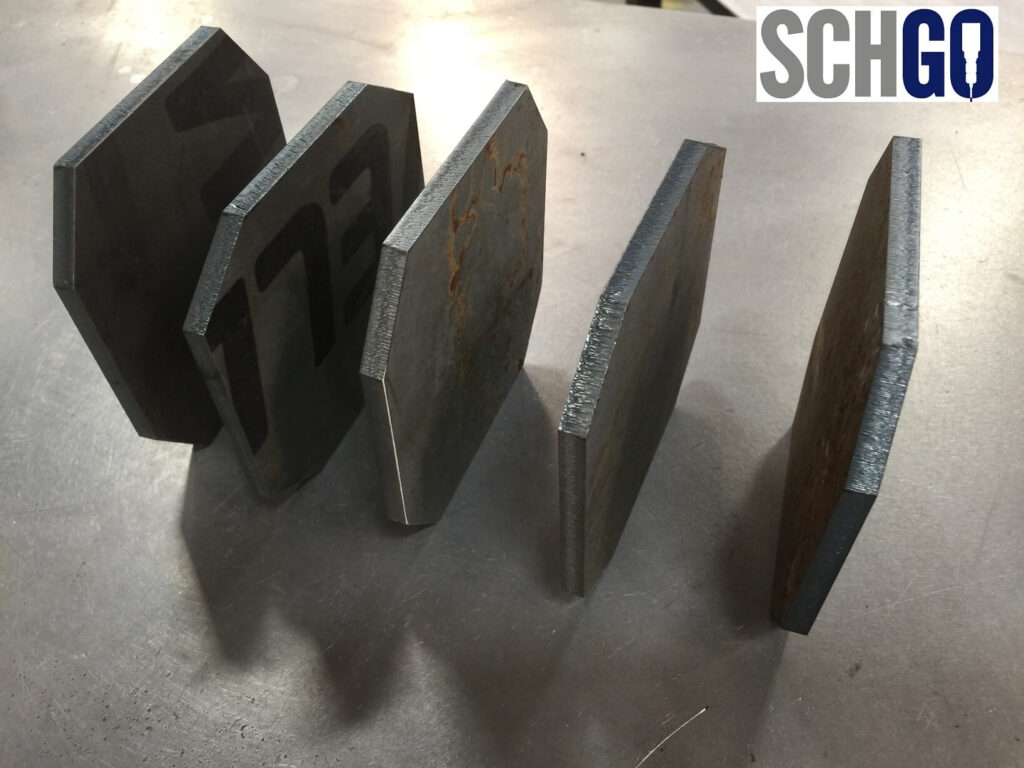

Implementing Robust Quality Assurance Practices: To ensure the highest standards of quality and consistency in your precision engineering projects, it’s essential to implement robust quality assurance practices. This includes establishing clear quality control procedures, training personnel on quality standards and inspection techniques, and continuously monitoring and improving processes to identify and address areas for improvement.
Quality control and inspection are essential components of precision engineering, ensuring that products meet the highest standards of quality, reliability, and performance.
By implementing the quality control and inspection methods outlined in this guide, you can uphold the highest standards of quality in your precision engineering projects and deliver exceptional results to your customers.
At SchGo Engineered Products, we’re committed to helping you achieve excellence in precision engineering through our comprehensive range of quality control and inspection services.